NOAA Updates its Seasonal Outlook on March 21, 2024 – Hints of a Possibly Very Strong La Nina Coming: Published March 22, 2024
Updated at 11 p.m. EDT March 22, 2024. Three additional graphics were added plus some additional commentary.
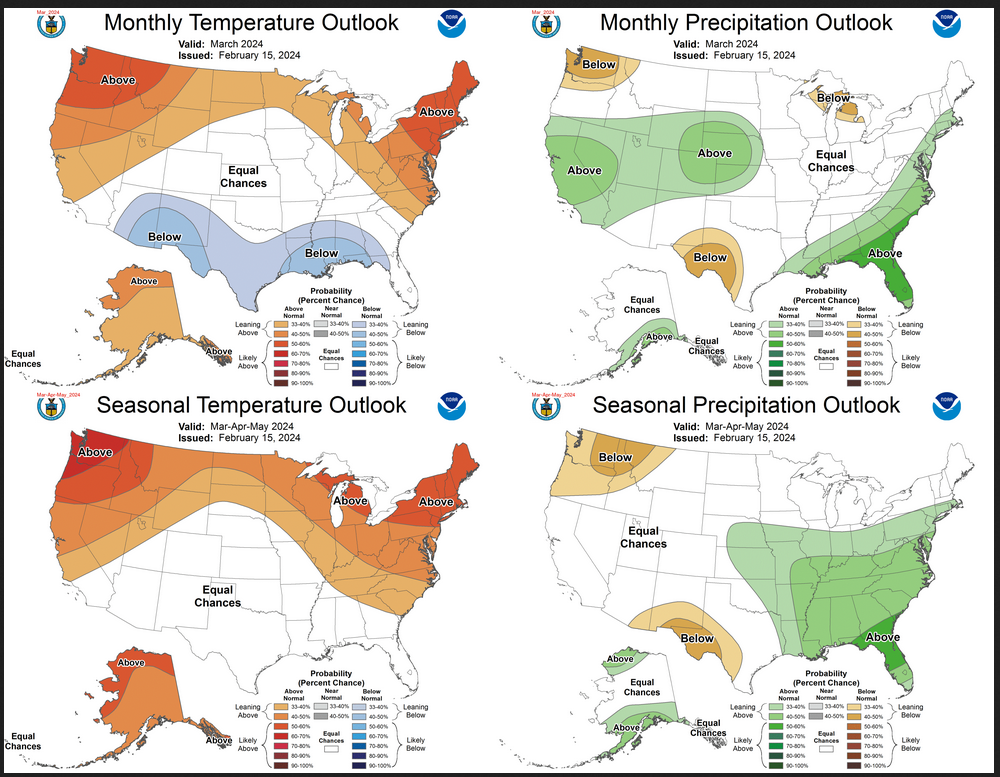
On the third Thursday of the month right on schedule NOAA issued their updated Seasonal Outlook which I describe as their Four-Season Outlook because it extends a bit more than one year into the future. The information released also included the Mid-Month Outlook for the following month plus the weather and drought outlook for the next three months. I present the information issued by NOAA and try to add context to it. It is quite a challenge for NOAA to address the subsequent month, the subsequent three-month period as well as the twelve successive three-month periods for a year or a bit more.
With respect to the long-term part of the Outlook which I call the Four-Season Outlook, there is a fairly rapid transition from El Nino to ENSO Neutral to LaNina. So getting the timing right is very challenging. The potential for a very strong La Nina is discussed but it is not the likely scenario at this point in time. But it seems that the longer-term outlook now factors in both drier conditions in certain parts of the U.S. and wetter conditions on the East Coast and Southeast this summer.
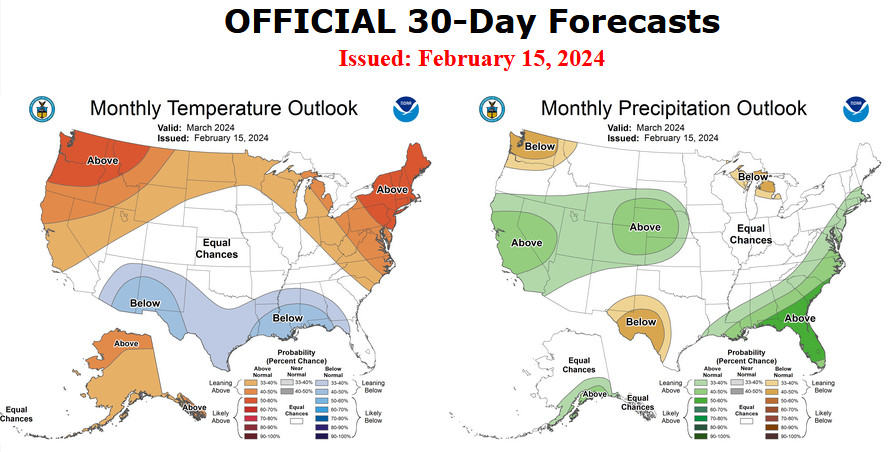
First, Let’s Take a Look at the (mid-month) Outlook for April.
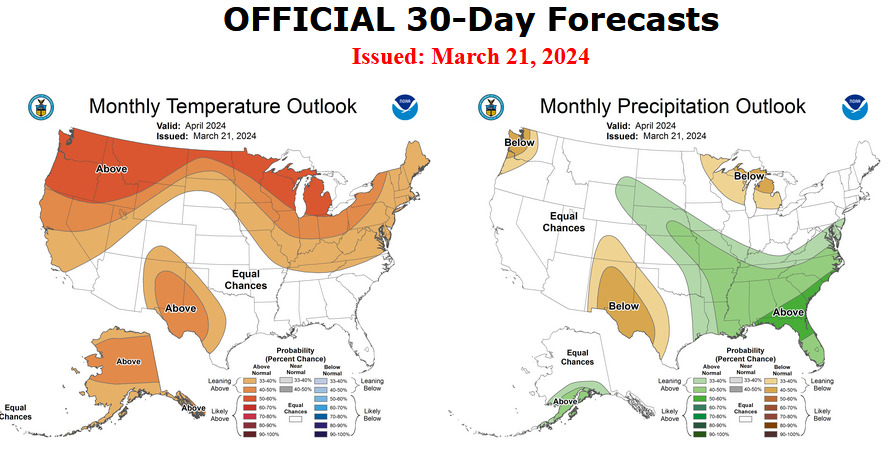
It will be updated on the last day of March

The top row is what is now called the Mid-Month Outlook for next month which will be updated at the end of this month. There is a temperature map and a precipitation map. The second row is a three-month outlook that includes next month. I think the outlook maps are self-explanatory. What is important to remember is that they show deviations from the current definition of normal which is the period 1991 through 2020. So this is not a forecast of the absolute value of temperature or precipitation but the change from what is defined as normal or to use the technical term “climatology”.
| Notice that the Outlook for next month and the three-month Outlook are somewhat different, especially with regard to temperature. This tells us that May and June will be different than April to some extent. |