Our Report on the JAMSTEC Three-Season Forecast – Posted on January 17, 2024

The Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, or JAMSTEC, is a Japanese national research institute for marine-earth science and technology
From the JAMSTEC Discussion:
“The recent observation suggests that the El Niño reached its peak. The SINTEX-F ensemble mean predicts that the El Niño will decay and an El Niño Modoki will develop and persist at least until the next boreal spring. The model also predicts that a La Niña Modoki will occur in boreal autumn. However, there is a large uncertainty in the predicted amplitude.”
Although it is a World forecast, it includes a forecast for North America since North America is part of the World.
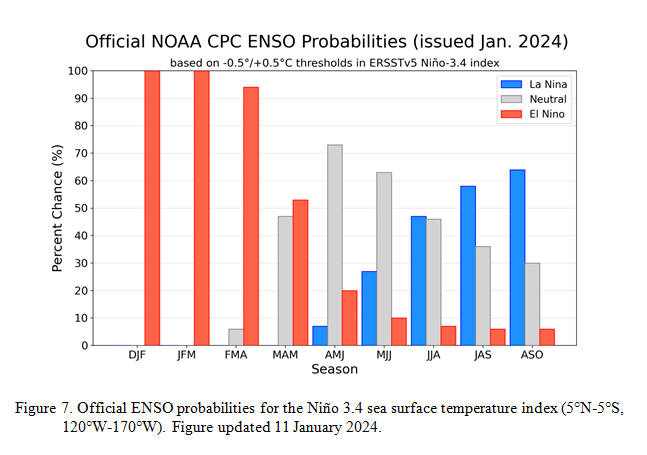
First, we take a look at the forecasted sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTA). JAMSTEC starts by forecasting the SSTA and Nino 3.4 Index on the first day of the month and from there it usually takes their models about two weeks to produce their seasonal forecast. I received it from JAMSTEC on January 10, 2024 which is a week before when NOAA will issue their Seasonal Update this month but I had so many articles to publish that I did not publish this JAMSTEC forecast immediately. The JAMSTEC model runs are based on conditions as of January 1, 2024. The NOAA Seasonal Outlook will be based on conditions closer to the time when it is issued.
We have a full three-season forecast from JAMSTEC this month. We also have single-month forecasts for February, March and April 2024.
Let’s take a look.
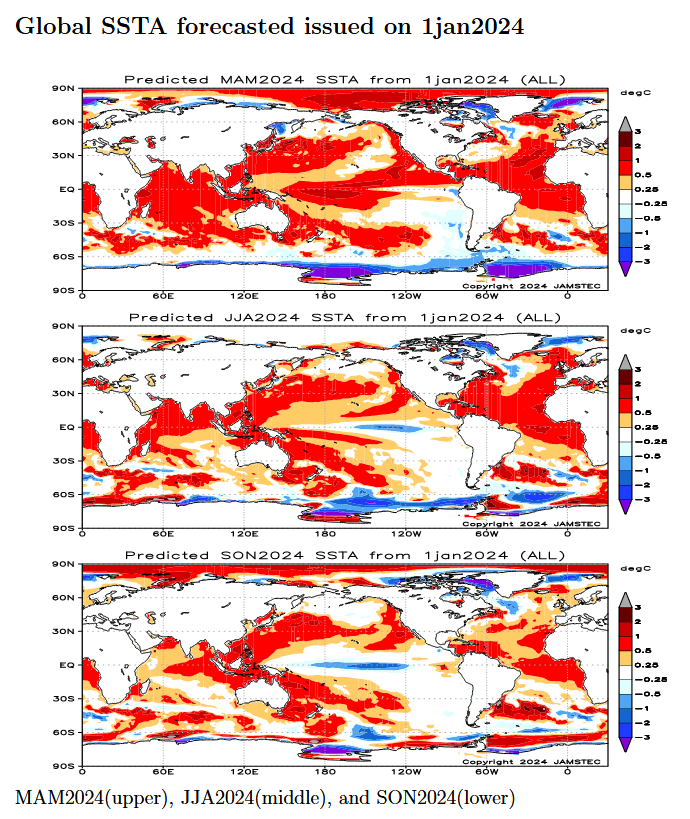
| This shows their forecast of sea surface temperature anomalies at three points in time. Red is warm and is associated with El Nino if it occurs in the Nino 3.4 measurement areas. You can see the El Nino tongue of warm water extending from Peru to the west in the MAM image but look at that blob of warm water to the west i.e. by this point in time this has Modoki characteristics which impact the Walker circulation. JJA and SON show ENSO Neutral or La Nina.
JAMSTEC (and also NOAA) are showing very warm oceans in many parts of the world. I have written about that before. It raises questions about the reliability of our current approach to thinking about the ENSO Cycle. This is covered in another article that can be accessed HERE. But JAMSTEC is showing a relatively normal ocean off the coast of much of the U.S. which probably explains their strange forecast. JAMSTEC uses the same definition of Normal (climatology) as NOAA. JAMSTEC does a better job at characterizing La Ninas and El Ninos than NOAA. JAMSTEC provides me with a lot of other information that I do not include in my articles to keep them to a manageable size for readers. JAMSTEC has been having some computational issues with its model. From the email I received from them: “Because of changes to the library in our computer, this time we could not complete all members”. Last month they were not able to publish at all. I do not know how to assess their message to me. In November they upgraded their model from 12 members to 36. Their goal is to go to 108. On the website, the images indicate that all members were included. It is not possible to accurately estimate the current conditions. So the technique in ensemble models is to perturb the assumptions slightly for multiple model runs (or use different physics models for some runs) and take the average (mean) of the solutions. Each solution is called a member of the group of solutions for which the mean was taken. I am intrigued by the coincidence of this “change to the library in our computer” with their publication of this article. Based on the Japanese Culture they would not have released this forecast if they did not have confidence in it. |
Some Readers will have to click on “Read More” to read the rest of the article which you need to read to see the forecasts. I can only include a certain amount of material in the lede.